Jaundice, characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels in the blood, is a common condition among newborns. While often benign, it requires careful monitoring and sometimes intervention to prevent complications. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, the treatment of jaundice in newborns.
Understanding Jaundice in Newborns
Jaundice occurs when bilirubin, a yellow pigment formed from the breakdown of red blood cells, builds up faster than a newborn’s liver can break it down and excrete it through stool. In most cases, this condition appears within the first week of life and typically peaks around the third to fourth day.
Causes of Neonatal Jaundice
Several factors contribute to the development of jaundice in newborns:
1. Physiological Jaundice: This is the most common type, occurring in over half of all newborns. It arises because a newborn’s liver is not yet fully matured to efficiently process bilirubin.
2. Breastfeeding Jaundice: Occurs when inadequate breast milk intake leads to dehydration and reduced bilirubin elimination.
3. Breast Milk Jaundice: A less common condition where certain substances in breast milk disrupt bilirubin metabolism.
4. Blood Group Incompatibility: Such as Rh or ABO incompatibility between mother and baby can cause increased breakdown of red blood cells, leading to higher bilirubin levels.
5. Infections, Liver Diseases, and Genetic Disorders: Rarely, underlying medical conditions can contribute to jaundice in newborns.
Symptoms of Jaundice
The primary symptom of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. Other signs may include:
- Pale stools
- Dark urine
- Excessive sleepiness or poor feeding
Diagnosis of Neonatal Jaundice
Diagnosing jaundice involves assessing the baby’s skin color and may require a blood test to measure bilirubin levels accurately. Depending on the severity and underlying cause, additional tests such as blood group testing and Coombs test may be performed.
Treatment Options for Neonatal Jaundice
The management of jaundice in newborns aims to prevent the harmful effects of bilirubin on the developing brain while determining and treating the underlying cause.
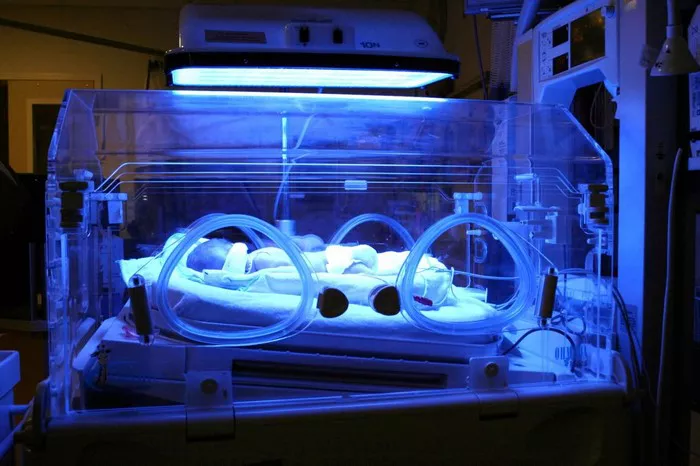
1. Phototherapy
Phototherapy is the cornerstone of treatment for neonatal jaundice. It involves exposing the baby’s skin to special blue lights that help convert bilirubin into a form that can be excreted in the urine and stool. Key points about phototherapy include:
Types of Phototherapy: Conventional phototherapy and intensive phototherapy are the two main types, with intensive phototherapy being more effective in reducing bilirubin levels.
Duration of Treatment: The duration depends on the baby’s age, bilirubin levels, and response to therapy. Phototherapy is usually continued until bilirubin levels decrease to a safe range.
Monitoring During Treatment: Regular monitoring of bilirubin levels and the baby’s hydration status is essential during phototherapy to ensure effectiveness and safety.
2. Exchange Transfusion
In severe cases of jaundice where phototherapy is ineffective or when bilirubin levels are dangerously high, exchange transfusion may be necessary. This procedure involves slowly withdrawing small amounts of the baby’s blood and replacing it with donor blood or plasma to reduce bilirubin levels rapidly.
Indications for Exchange Transfusion: These include extremely high bilirubin levels that pose a risk of brain damage (kernicterus) and cases where the baby shows signs of acute bilirubin encephalopathy despite phototherapy.
Risks and Complications: Exchange transfusion carries risks such as blood clotting, infections, and changes in blood chemistry, necessitating careful monitoring and experienced healthcare providers.
See Also: Can Jaundice Go Away on Its Own in Newborns?
3. Supportive Care
In addition to specific treatments like phototherapy and exchange transfusion, supportive care plays a crucial role in managing jaundice in newborns:
Feeding Support: Ensuring adequate breastfeeding or formula feeding helps prevent dehydration, which can worsen jaundice.
Monitoring: Regular monitoring of the baby’s weight, urine output, and feeding patterns is important to detect any worsening of jaundice early.
Parent Education: Educating parents about the signs of jaundice, the importance of feeding, and when to seek medical help is essential for early intervention and management.
4. Addressing Underlying Causes
For cases of jaundice due to factors like blood group incompatibility or infections, addressing the underlying cause is crucial:
Rh Incompatibility: Rh-negative mothers may receive Rh immunoglobulin during pregnancy and after delivery to prevent sensitization and subsequent hemolytic disease in subsequent pregnancies.
ABO Incompatibility: Monitoring bilirubin levels closely and providing appropriate treatments such as phototherapy or exchange transfusion when necessary.
5. Long-term Follow-up
Even after jaundice resolves, some babies may require long-term follow-up to monitor for potential developmental issues associated with severe jaundice. Early intervention programs and developmental assessments may be recommended for at-risk infants.
Conclusion
In conclusion, jaundice in newborns is a common condition with various causes ranging from benign to potentially serious. Timely identification and appropriate management are essential to prevent complications such as kernicterus and ensure the baby’s healthy development. Phototherapy remains the mainstay of treatment, while exchange transfusion is reserved for severe cases. Supportive care and addressing underlying causes play pivotal roles in managing neonatal jaundice effectively. With advances in medical technology and vigilant monitoring, the prognosis for most infants with jaundice is excellent, highlighting the importance of comprehensive newborn care protocols.
By understanding the nuances of neonatal jaundice and staying informed about current guidelines and treatments, healthcare providers and parents can work together to ensure the best outcomes for newborns affected by this common yet manageable condition.